The World Wide Web is a wonderful place that offers virtually endless possibilities for E-commerce, information exchange, networking, or entertainment.
Unfortunately, not everyone online is sincere and trustworthy. This is why websites and email servers need to implement strong Security Measures that will protect their users and visitors.
It establishes trust between you and your customers or visitors.
Google will rank your website higher with SSL certificates.
You show that you take all information seriously to protect sensitive information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, licenses, and passwords.
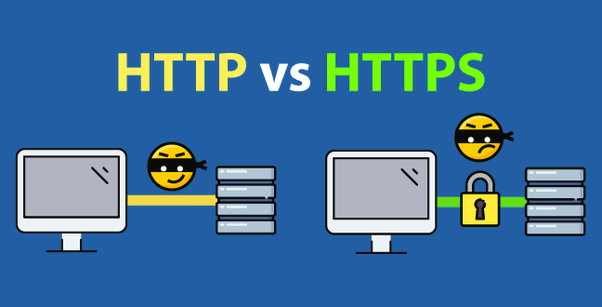
All pages with sensitive information are protected by SSL Certs running with HTTPS instead of HTTP in your browser.
This will help stop tampering with or changing the data contained in communications to and from your website.
Showing a Site Seal demonstrating that an SSL Certificate is active on your website and that anyone can verify the ownership and security of your website.
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web. It defines how messages are formatted and transmitted between web browsers, Web Servers, and other devices. When a user enters a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) into a browser's address bar and presses enter, the browser sends an HTTP request to the server hosting that webpage. This request specifies the action to be performed, such as retrieving a webpage or submitting form data. The server, upon receiving the request, processes it and returns an HTTP response, which includes the requested content along with status information (e.g., success or error codes). HTTP operates over a stateless connection, meaning each request from the client is independent and does not retain information from previous requests. This simplicity makes HTTP efficient for retrieving web pages and resources but requires additional mechanisms like cookies or session management for maintaining user state across multiple requests. Originally designed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, HTTP has evolved through various versions, with HTTP/1.1 being widely used until the introduction of HTTP/2 and subsequent improvements in performance and security. Despite its fundamental role in web communication, the lack of encryption in HTTP makes it susceptible to security vulnerabilities, prompting the widespread adoption of HTTPS for secure data transmission.
Information is exchanged between clients and servers in the form of hypertext documents, from which HTTP gets its name. The HTTP protocol transfers resources across the internet between the client devices and Web Servers. It starts with a client machine sending requests in the HTTP format. The server machine receives the request, understands it and takes appropriate action. The response again has to be formatted in a specific manner adhering to the HTTP protocol for the client device to deliver the content properly.
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, serves as the foundational protocol for communication on the World Wide Web. Its key characteristics define how information is exchanged between a client (typically a web browser) and a server. Firstly, HTTP operates in a stateless manner, meaning each request-response cycle is independent, lacking memory of previous interactions. This simplicity allows for efficient communication but necessitates additional mechanisms for maintaining session state, such as cookies or server-side sessions. Secondly, HTTP transfers data in plain text format, which simplifies debugging and troubleshooting but poses security risks as data can be intercepted and read by malicious entities.
Communication between clients and servers is done by requests and responses. They are listed as following.
A typical HTTP request and response sequence for a webpage begins when a user enters a URL in their web browser and hits enter. The browser initiates an HTTP request to the server hosting the requested webpage. This request includes details such as the type of request (GET, POST, etc.), the URL, and any additional parameters. Upon receiving the request, the server processes it and retrieves the necessary resources, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other files. The server then constructs an HTTP response containing these resources along with status information (e.g., 200 OK for successful requests) and sends it back to the user's browser. The browser interprets the response, renders the webpage based on the received resources, and displays it to the user. This seamless exchange illustrates the fundamental workings of HTTP in delivering content across the web.
When a website using HTTP is protected by SSL, it inherits the letter S at the end.
HTTPS keeps your information secured in two separate ways
It encrypts your data to make it impossible to obtain your private information
It also provides a reliable identification mechanism that the site you are visiting is not an impostor.

HTTPS or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is just a secure version of HTTP. This is the primary protocol used today to send data between a web browser and a website. HTTPS is encrypted in order to increase security of data transfer. This is particularly important when users transmit sensitive data.
HTTPS was created by Netscape Communications in 1994. They created it for their Netscape Navigator Browser. HTTPS was originally used with the SSL protocol. As SSL evolved into Transport Layer Security (TLS), HTTPS was formally specified by RFC 2818 in May 2000. In 2018 Google announced it's Chrome browser would mark HTTP websites as "Not Secure". This was to encourage all websites to implement HTTPS, as an effort to make the World Wide Web a safer and more secure Internet.
The phrase or word hypertext originally came from Ted Nelson in 1965. The original HTTP was developed and originally proposed by Tim Berners-Lee, the director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The W3C's mission is to lead the web to its full potential by developing protocols and guidelines that ensure the long-term growth of the web.
When you connect to an HTTPS Secured website, your web browser will check the Website's security certificate, and verifies it was issued by a legitimate certificate authority. This helps you ensure that if you see the "HTTPS in your web browser’s address bar, you are actually connected to a secure website.
HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, builds upon HTTP with enhanced security features crucial for modern web communication. The primary characteristic of HTTPS is its use of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption protocols. This encryption ensures that data exchanged between a client (such as a web browser) and a server remains confidential and secure against interception by third parties. HTTPS also provides authentication mechanisms, verifying the identity of the website to ensure users are connecting to legitimate servers and not imposters. This verification is facilitated through digital certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs), which validate the authenticity of the website's identity. Additionally, HTTPS enhances user trust by displaying indicators such as a padlock icon or "Secure" label in the browser's address bar, indicating a secure connection.
The HTTPS protocol is called Transport Layer Security (TLS). Also known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). This protocol secures communications by using what is known as an asymmetric public key infrastructure. This type of security system uses two different keys to encrypt communications between the two parties.
The Web Server calculates a cryptographic hash of the document’s contents, included with its digital certificate. Which the Browser can then independently calculate to prove that the document’s integrity is intact. Together this will help guarantee the encryption, authentication, and integrity of the web pages making HTTPS requests are a much safer protocol for browsing and conducting business on the web than standard HTTP.

You are making your website more secure.
HTTPS is not like a web application firewall
If you are using a Content Management System (CMS) such as WordPress, or you have any other login where you host any kind of sensitive data
Then setting up a secure HTTPS login is the best precaution you can take.
HTTPS is the basic price of security. It is the very minimum you can offer your visitors.
Aside from security, HTTPS also will provide your visitors a trust factor.
There is evidence that the use of SSL can improve lead generation by over 40 percent.
According to research performed by GlobalSign, more than 87 percent of respondents would abandon a purchase if there was no HTTPS in use.
Not only do your visitors pay attention to your site's security,
But so does Google. Security is at the heart of what Google does these days
That’s why Google has listed HTTPS as a ranking factor.
Switching to HTTPS is fairly straightforward for smaller websites
For larger websites, it can be more complicated, from an SEO perspective, and requires skilled technical staff to make the changes.
Google has started dropping websites who are not using HTTPS in their search results. Without search engines like Google and Bing, no one will find you.
If your website is not encrypted it is vulnerable to man-in-the-middle and eavesdropping attacks, which can let attackers gain access to website accounts and sensitive information, and modify webpages to inject malware or advertisements.
HTTPS is designed to withstand such attacks and is considered secure against them.
Using HTTPS will increasingly be the norm rather than the exception. Plan to migrate sooner rather than later.
If you are convinced of the benefits of HTTPS and are considering making the switch for your website.
Below are the steps to help you navigate the transition:
HTTPS is the bare minimum level of protection that any website should use. It is not just for eCommerce stores or online banking, it is becoming very common among all types of sites, even Informational sites that collect information from the visitor.
Most all websites will be using HTTPS in favor of HTTP, and we can only hope that another SSL type protocol will be developed that will be even more secure. Website owners who take the time and effort to enact HTTPS are more likely to be more successful. According to numerous studies and surveys the vast majority of shoppers would abandon a website that is not using the HTTPS protocol.
Joel is a expert in the fields of digital, technology, and business. With a wealth of experience and knowledge, he has successfully navigated...
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
Tweet Share Pin Email
Comments