A content management system (CMS). Allowing you to build websites and blogs where the content and the design are independent. Providing you with incredible flexibility.
The WordPress Dashboard is essentially the control panel for your entire WordPress website. It is where you can create and manage content, add functionality in the form of plugins, change styling in the form of themes, create posts, media library, pages, comments, appearance options, plugins, users, tools, settings and so much more.
You can choose from thousands of pre-made free or paid themes. These can be found at the WordPress.org theme repository. Or you can access themes right through the WordPress Dashboard.
You can install WordPress to your own WordPress Website through one of the following options:
Download a free instance of WordPress and installed it on your hosting account. Follow the instructions at WordPress.org.
Or install WordPress via Softaculous through cPanel with just a few clicks of your mouse
RSH Web Services would also be glad to install WordPress on your website with no extra charge.
When you open the WordPress Dashboard for the first time, you might be overwhelmed
Do not worry, once you start to look around it will start to become very familiar to you.
You can reach your Dashboard by going to https://"Your_Domain".com/wp-admin.
Site Name
In the top left corner, you will see the name of your WordPress website.
Gravatar
In the top right, you will see your username and Gravatar image, (if any).
If you do not already have one, you should create a Gravatar account. This allows you to have an avatar or photo associated with all of your blog posts, both on this website, and any other WordPress websites you build or contribute content or comment on.
In the left column these are the first options you see.
This is the section where you create and manage the content for your site.
Posts and Pages are your “text” content, while media is for images and other files.
Comments, of course, are the comments people can leave on your blog posts.
You can click on “All Posts” or “All Pages” to see existing content, or “Add New” to start a new one.
But wait! When you create a new post or page, you will see very similar editing windows. So why are there two?
The distinction between Posts and Pages usually confuses people new to WordPress.
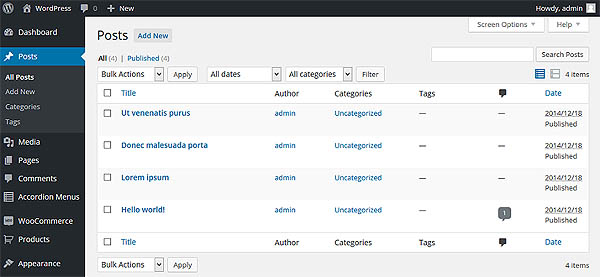
Posts: Are dated content (think blog posts) with author information and can be displayed in reverse chronological order on a blog within your overall site. You can also use them for press releases, product updates, or anything that should have a date attached (or you can choose to hide the dates if you wish). Posts also allow you to set Categories, and Tags.
Pages: are your static content pages. These are your home page, your “About Me” page, your “Contact” page, and anything else you might want to put in your main navigation menu. (You can also have pages that are not in your menu, but they work the same either way). Unlike posts, pages generally do not have a date or author attached to them.
Media: This is where you will find your media library such as photos, graphics, PDFs, sound, and videos. After you add to your Media Library, you can then drop any of that content into a post or page.
Comments: Where you can find all the pending and published comments. You will see a bubble to let you know when there’s a new comment to approve. You can approve comments as is or edit them.
Feedback is where your "Contact" form content (if any) will reside.
This is the second set of options in the left column, you will use them to manage your website's appearance and functionality.
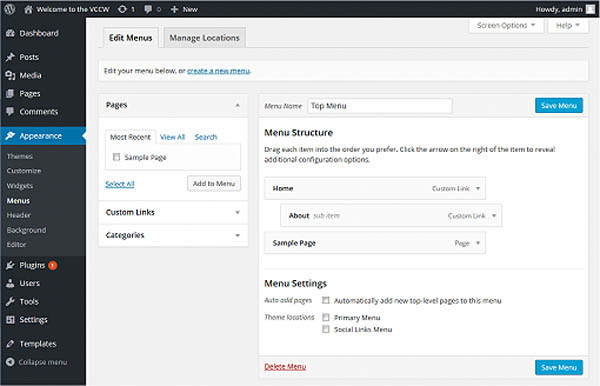
Your Appearance tab has a number of options.
Themes: Choose from one of the many free options at WordPress.org, or upload one you purchased elsewhere in a .zip format.
Customize: This feature provides a separate menu. You can change settings within your designated theme, as well as set a logo and background color or pattern. The options here will vary considerably between themes, and will reset if you activate a different theme, so be forewarned.
Widgets: These are bits of content you can drop into a blog sidebar or add to your page’s header or footer.
Menus: Will give you the ability to choose which pages to display in your main navigation menu, put them in your preferred order, and even create drop-down sub menus.
Header: Customizing, but only for your header information. Some versions of WordPress will include Header within Customize.
Editor: The one place you can really mess things up
Proceed With Caution. This is where you can modify the CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) for your theme.
You can also add plug-ins. There are plugins for automatic backups, plugins for additional security, plugins to change how social media and images are handled and so much more.
There are thousands of plugins to pick from, and many are free. And again, many are available through the WordPress.org plugin repository or in your Dashboard.
Some of our Blogs about plugins.
Here you will find settings for some of your basic website functionality.
Users: This option allows you to create additional user roles for your website.
Tools: Gives you the option to import or export all the content of your website. Your posts, pages, media, and comments. This is handy if you are moving your website. (It doesn’t allow you to migrate your theme or plugins, however.).
Settings: This is where you can set the time zone, change display options, set your homepage name, and more. Your theme and plugins may add more settings here, and your hosting provider may also include additional tools.
For a more complete look at the WordPress Admin Dashboard, check out First Steps with WordPress from our friends at WordPress.org
You can also check out the WordPress Codex online manual for WordPress, which covers every topic you could ever think of. In particular, the page on Administration Screens will offer more details on the items addressed in this article.
The WP admin dashboard is the central point where you have control of most elements in WordPress. This panel provides information in regards to what is going on in your website.
With WordPress you not only can create a good website but also to update its content fairly easily. You can edit web pages, posts, add new users, customize the site appearance with themes and plugins, and much more.
A senior content writer for RSH Web with a fondness for composing engaging and informative articles. In addition to...
We'd love to hear your thoughts! Feel free to share your experiences or ask any questions in the comments below.
This policy contains information about your privacy. By posting, you are declaring that you understand this policy:
This policy is subject to change at any time and without notice.
These terms and conditions contain rules about posting comments. By submitting a comment, you are declaring that you agree with these rules:
Failure to comply with these rules may result in being banned from submitting further comments.
These terms and conditions are subject to change at any time and without notice.
Tweet Share Pin Email
Comments